|
Basic Principal
Ground Penetrating Radar (GPR) uses a high frequency radio signal that is transmitted into the ground and reflected signals are returned to the receiver and stored on digital media. The computer measures the time taken for a pulse to travel to and from the target which indicates its depth and location. The reflected signals are interpreted by the system and displayed on the unit’s LCD panel. |
 |
| GPR Data Collection (below ground)
In order to find the location and depth of an object buried subsurface various types of GPR equipment is used to collect the data. The type of GPR equipment required is dependent on the depth and size of the target to be located. The radar unit emits and receives reflected signals up to a thousand times per second. These signals are viewed by the field operator on location immediate analysis and are also stored in the system and downloaded to a computer for further data analysis if required. |
 |
| GPR Data Collection (in concrete)
To locate objects such as rebar, conduits and post-tension cables imbedded in concrete a high frequency GPR systems is used. The data can be collected in simple line scans to determine the thickness of concrete or in a grid format which will produce a map of any targets located in the concrete. Using this method we can look at virtual slices in the image to determine the depth of the objects and create a 3D map of the image. |
 |
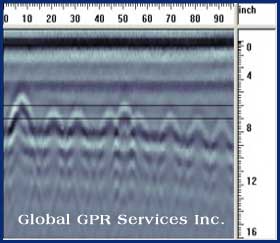
| GPR Data Analysis
GPR waves travel through many different materials. Different types of soil, concrete, fill material, debris, and varying amounts of water saturation all have different dielectric and conductive properties that affect the GPR waves, and thus GPR data interpretation. Although the data images are displayed on the screen they still require someone with field experience to interpret them in order to accurately determine the findings. |
 |
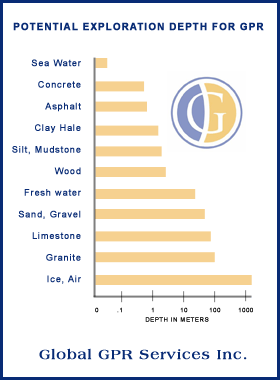
| How Deep Can It Go?
This is probably one of the most commonly asked questions. In most cases an estimated depth range can be determined with accuracy based upon the subsurface material and the frequency of the GPR antenna. For applications requiring higher resolution, such as locating rebar or conduits in concrete, a higher frequency GPR system (1,000 MHz) is used. This will give high resolution detail for down to approximately 24 inches in depth. Applications which require deeper penetration in ground soil requires a lower frequency (12.5 MHz to 500 MHz). Depending on the subsurface material the depth range can be from a few inches to thousands of feet (as indicated in the chart). |
 |
* Contact us if you require additional information regarding ground penetrating radar technology.




![[click to call]](http://www.ringcentral.com/ringme/55852922/1/click-to-call-small-o.gif)